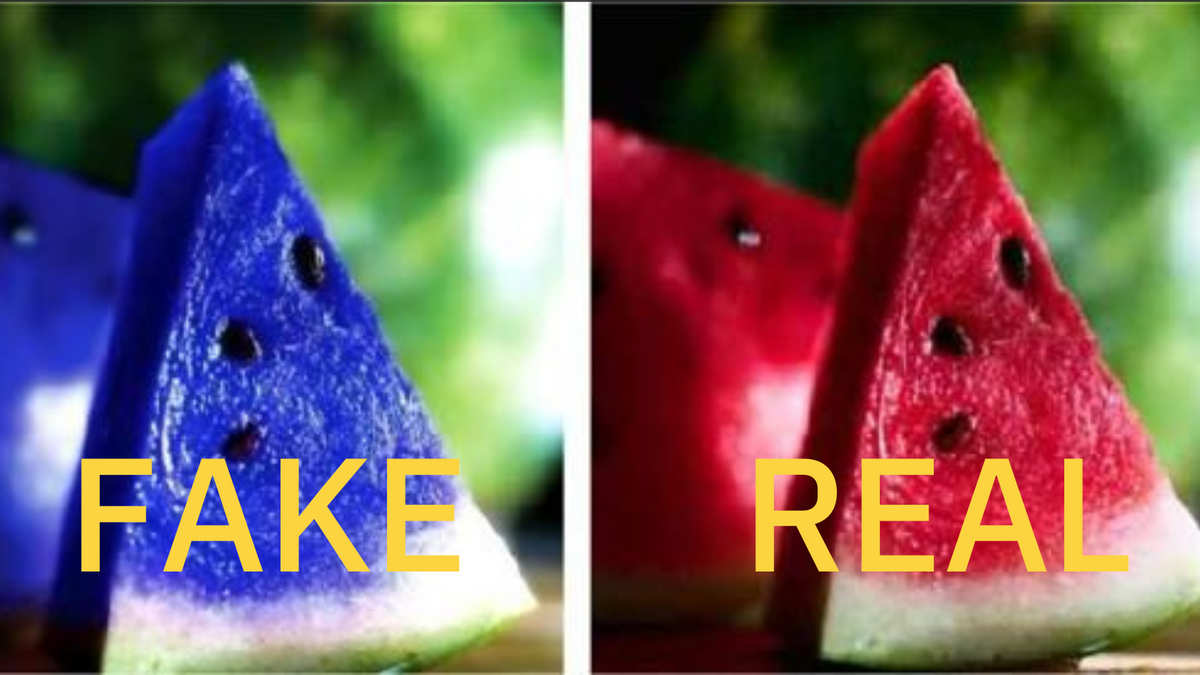
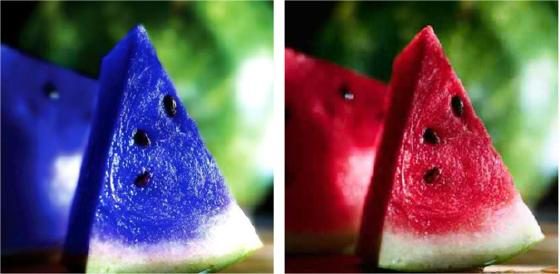
In January 2014, Snopes came across this photo on Pinterest:
The caption read:
Moonmelon (scientifically known as Asidus). This fruit grows in some parts of Japan, and is known for its vibrant blue color. What you probably don’t know about this fruit is that it can switch flavors after you eat it. Everything sour will taste sweet, everything salty will taste bitter, and it gives water a strong orange-like taste.
Alas, there is no delectable blue fruit that grows in Japan, causes “flavors to switch” after you eat it, and costs about 16,000 yen (roughly $200). This jape has been spread multiple times on social media outlets such as Pinterest and Twitter in the last few years, and it’s simply a made-up story attached to an ordinary photograph of a watermelon slice that has been tinted blue:
However, there is a real “red miracle berry” fruit (Synsepalum dulcificum) that produces a protein known as “miraculin” that can cause other sour foods subsequently consumed to taste sweet:
Popping a squishy red miracle berry into your mouth is almost like hacking your taste buds. For up to an hour, the juices coat your tongue and previously sour foods like lemon and vinegar magically taste deliciously sweet.
The berry and its plant (Richardella dulcifica) grows in West Africa. While the local population has been using its miraculous properties for centuries, it was only in 1968 that the all-important protein miraculin was extracted and sold in tablets. They’re now available the web and often feature in “taste tripping” parties where brave souls dine on pickles and limes.
The miraculin also toys with sweet, sugary food in interesting ways. Drop a load of aspartame after popping a miracle berry tablet and the miraculin represses your sweet receptors, making sweet foods taste bland. But in a slightly more acidic environment, the receptor’s response skyrockets, making aspartame taste sweeter than ever though possible.
[See also on Snopes: Are Pink, Fuzzy Bananas a Real Thing?]